How Digital Literacy in India Moved from Basic to a Core Skill

From Learning Basic Computer Tricks to Adapting Digital Fluency and Everyday Tech Habits
There was a time when learning MS Word or typing on a keyboard was a big deal. Now? That’s just the starting line. Digital literacy skills have expanded way beyond clicking icons — they cover social media awareness, using online payments safely, and even knowing what’s fake news.
People across India now use phones to file taxes, attend classes, or even consult doctors online. This means every citizen needs some level of digital fluency, not just access to gadgets. It’s become part of daily life — kinda like knowing how to ride a bike, only with Wi-Fi.
Government-Led Digital Literacy Programs That Pushed the Digital India Dream Forward
The Digital India mission, PMGDISHA (Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan), and BharatNet have played a huge role in bridging the digital gap. These programs trained millions in basic computer use, cybersecurity, and online communication.
Urban areas picked it up fast, but rural India’s catching up too. You’ll see small villages with Wi-Fi spots and kids teaching elders how to use WhatsApp or UPI. This blend of policy, youth enthusiasm, and tech curiosity made digital empowerment in India real and visible.
Why Digital Literacy Became a Core Life Skill

Digital Skills Fuel Jobs, Careers, and New Earning Paths in a Tech-Driven Economy
Employers today look for candidates who can handle online tools and virtual communication. Whether it’s running an online store or managing customer chats, digital literacy drives employability.
Take small-town freelancers — many now find work through digital platforms. Even farmers use apps for market prices. The impact of digital literacy in India is clearly tied to job growth, especially for youth. In short, you don’t just need a degree anymore — you need Wi-Fi confidence.
Digital Literacy Powers Banking, Shopping, Health, and Everyday Services for All
From UPI payments to telemedicine, everything’s digital now. People can buy groceries, pay electricity bills, or book doctor appointments with a few taps. Even senior citizens are slowly getting into the groove.
Being digitally literate means being independent. No more waiting in lines or relying on others for simple stuff. It’s not about being techy — it’s about making life smoother, faster, and smarter.
The Broader Impact of Digital Literacy on India’s Society and Economy
How Digital Skills Empower Women and Marginalized Communities Across Rural Areas
Women in rural India once had limited exposure to digital tools. Now, through initiatives like Digital Sakhi and NGO-led training, they’re managing small businesses, selling crafts online, and even teaching others.
This new form of digital inclusion has changed lives. A smartphone can be a mini office, a classroom, or even a marketplace. That’s empowerment in its raw form — tech breaking barriers.
Bridging the Urban-Rural Gap While Tackling Connectivity and Awareness Issues
Sure, India’s digital story shines bright, but there’s still work to do. Many villages face weak connections, limited access to devices, or language barriers. Local-language learning platforms and low-cost phones are helping though.
This urban-rural balance isn’t just about tech — it’s about fairness. The goal is a digitally literate India where everyone, from metros to small towns, gets equal access to opportunity.
Core Components Defining Digital Literacy and Responsible Online Citizenship
Why Critical Thinking and Fact-Checking Are the New Superpowers Online
Scrolling through social media, we see endless information — not all of it true. So part of being digitally literate is learning to verify facts, question sources, and think smartly.
Fake news spreads fast, and it’s often tricky to spot. Teaching information literacy in schools and workplaces helps people separate facts from fiction, protecting both democracy and daily decision-making.
Staying Safe Online by Practicing Responsible and Aware Digital Citizenship
Safety online isn’t only for tech experts. Everyone should know about phishing scams, strong passwords, and privacy settings. Parents now talk to kids about online behavior just like they talk about traffic safety.
Practicing safe digital citizenship builds trust and confidence. It also shapes a more responsible online community that respects privacy and understands consequences.
The Next Chapter of Digital Literacy

Why AI Tools and Next-Gen Tech Require Continuous Digital Upskilling
The rise of AI tools like ChatGPT and automation systems means tomorrow’s jobs will need new skills. Knowing how to use these tools safely and smartly will define the future of digital literacy in India.
AI isn’t replacing humans — it’s just demanding better awareness. Learning how to work with digital tools, not against them, will keep workers relevant and adaptable.
Schools, Parents, and Businesses Working Together to Build Digital Readiness
Schools can’t do it alone. Parents need to understand online education tools, and companies must train employees regularly. From digital education modules to short upskilling programs, collective effort makes the digital future inclusive.
Even small actions count — teaching grandparents how to pay online or kids how to stay safe online. Everyone’s a student here, learning together.
Building a Digitally Ready India for the Present and the Future
Digital literacy has become the new heartbeat of progress in India. It’s not just about knowing tech — it’s about using it smartly, safely, and responsibly. Whether it’s a farmer using an app, a homemaker running an online business, or a student learning coding — every story adds up to a stronger, digitally empowered India.
The next phase isn’t about gadgets. It’s about confidence, inclusion, and curiosity. The better we understand the tools in our hands, the brighter India’s future gets — pixel by pixel.
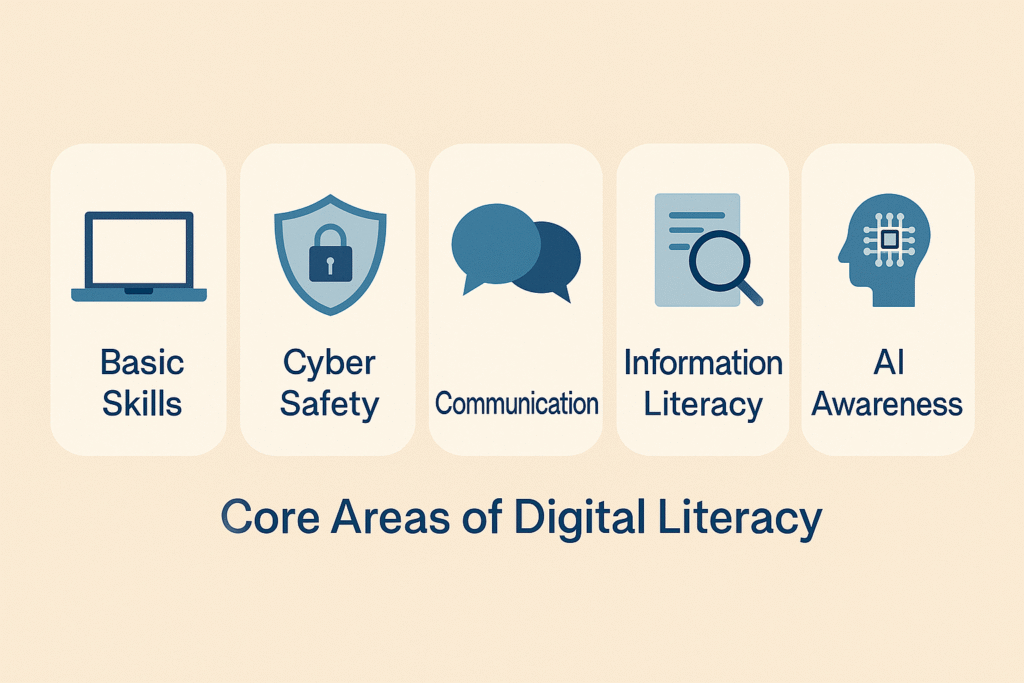
Quick Reference Table: Key Areas of Digital Literacy
| Area | Description | Relevance in India |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Skills | Using smartphones, browsers, apps | Foundation for daily life |
| Cyber Safety | Privacy, passwords, phishing | Protects individuals online |
| Digital Communication | Email, social media, messaging | Builds connection & work skills |
| Information Literacy | Fact-checking & verifying sources | Fights misinformation |
| AI & Automation Awareness | Using modern tools efficiently | Future career readiness |