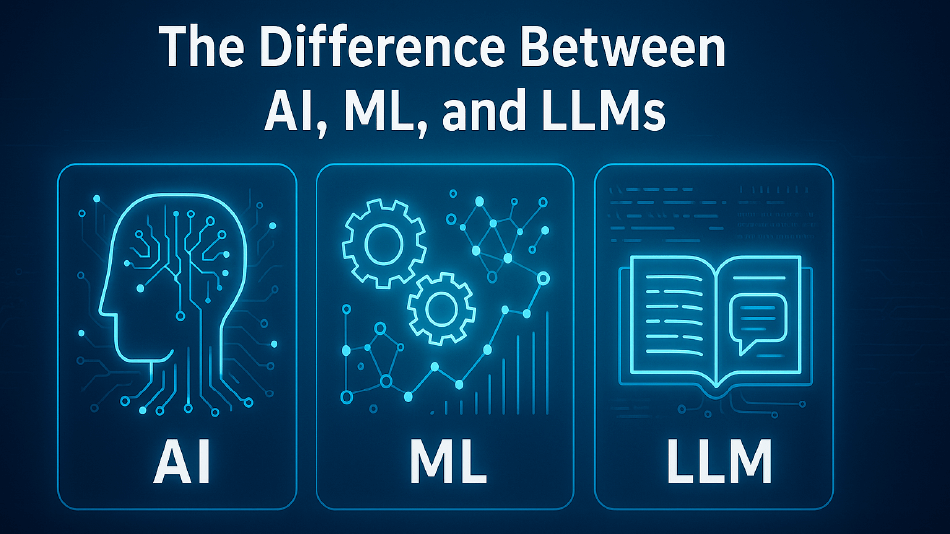
Ever get mixed up between AI vs ML vs LLM? You’re not alone. These three terms pop up everywhere — from tech talks to job ads — and it’s easy to think they all mean the same thing. But each one plays a different part in how machines “get smart.”
AI is the big idea — machines that can act smartly. ML is how they learn patterns from data. And LLMs? They’re the chatty ones that can read, write, and talk like humans. Folks often confuse them because they overlap and build on one another.
Now, in India, this stuff isn’t just happening in labs. It’s showing up in real life — like when you ask your phone for directions, get a Hindi chatbot reply from your bank, or see AI-powered health checks. From farming apps to e-learning platforms, these tools are quietly reshaping work and daily life.
Think of it like a family:
-
- AI is the parent — the broad idea.
- ML is the child that learns.
- LLM is the one who loves to talk and write.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is about building machines that can think and decide in a smart way. Instead of just following commands, AI tries to act like humans — noticing patterns, learning from data, and solving problems.
When your phone unlocks using your face, or your music app recommends a song you didn’t know you’d love, that’s AI in action. It’s not magic — just clever use of data and logic.
Simple Meaning and Real-World Purpose
AI means giving computers the power to “figure things out.” It’s when they learn, plan, and make choices — almost like people.
You can spot AI all around:
-
- Chatbots helping with customer support.
- Google Maps predicting the fastest route.
- Netflix showing shows based on what you watch.
- Smart cameras detecting motion or faces.
How AI Aims to Simulate Human Intelligence
AI tries to copy how humans think and react. When people learn from experience, they remember what worked — AI does that too.
AI systems mimic human skills like:
-
- Learning: Finding patterns from data.
- Reasoning: Making smart choices.
- Perception: Understanding images, voices, or text.
- Interaction Talking in human-like ways.
Narrow AI vs General AI
There are two main types of AI — narrow AI and general AI. They sound close, but they’re totally different. One exists now, the other is still just a dream.
Understanding Narrow AI
Narrow AI is built to do one thing really well. It can recognize a face, reply to messages, or predict the weather — but that’s it. It can’t suddenly learn to play cricket or write a song.
Examples of narrow AI include:
- Chatbots replying to customer questions.
- Voice assistants like Alexa or Siri.
- Email spam filters.
- Product suggestions on Amazon.
It doesn’t understand things — it just follows what it’s trained to do. Still, it’s everywhere and super useful in daily life.
What About General AI?
General AI would be like a machine that can do anything a person can. It could solve puzzles, plan your day, and even cook a meal — all without new training.
Right now, that kind of AI doesn’t exist. It’s still in research. Scientists haven’t cracked how to make machines think creatively, show emotions, or understand the world fully.
So for now, we live in the era of narrow AI — the kind that’s smart, but not human-smart.
Key Difference in a Nutshell
| Feature | Narrow AI | General AI |
|---|---|---|
| Skill | Focused on one task | Can handle any task |
| Examples | Chatbots, image recognition, spam filters | Human-like robots (theoretical) |
| Learning | Learns from specific data | Learns and adapts like humans |
| Status | Already used everywhere | Still in research phase |
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning is a type of AI that helps machines learn from data and improve automatically. Instead of being told exactly what to do, machines figure things out by spotting patterns.
For example:
-
- Your email learns which messages are spam.
- Online stores learn what you might buy next.
- Banks detect fraud by studying transaction patterns.
Main Types of Machine Learning
-
- Supervised Learning — the model learns from labeled data (like teaching with examples).
- Unsupervised Learning — it finds patterns on its own (like grouping similar items).
- Reinforcement Learning — the system learns through trial and reward (like a game).
How Machine Learning Works
It starts with data. The machine studies the data, finds rules, and makes predictions. Over time, it tests those predictions and adjusts itself — becoming smarter bit by bit.
ML helps companies forecast sales, detect diseases, and even recommend YouTube videos. The more data it sees, the better it gets.
What is a Large Language Model (LLM)?

A Large Language Model (LLM) is a special kind of machine learning model made to understand and generate text. Think of it as a super-smart reader and writer.
It’s trained on a huge collection of text — books, websites, chats — and learns how words connect. That’s why it can write essays, translate languages, summarize notes, or hold a conversation.
Examples include ChatGPT, Gemini, and India’s Krutrim.
How LLMs Work
An LLM breaks sentences into tokens (tiny word pieces). It predicts the next token based on context, just like how we guess the next word in a sentence.
It uses a transformer architecture — a design that helps it remember long conversations and make better guesses.
LLMs don’t “understand” like humans, but they’re great at sounding natural, writing fluently, and answering questions fast.
How LLMs Differ from Regular ML Models
| Feature | Machine Learning | Large Language Models |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Numbers, images, or labels | Text and language |
| Goal | Prediction and classification | Text generation and understanding |
| Training Size | Smaller datasets | Huge datasets (billions of words) |
| Example | Weather prediction | ChatGPT or Krutrim |
AI vs ML vs LLM — Side-by-Side Comparison
Here’s a quick way to see how they connect:
So, AI is the big field. ML lives inside AI. And LLM lives inside ML.
| Feature | AI | ML | LLM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Broad concept of smart machines | Subset of AI that learns from data | Subset of ML that works with language |
| Example | Self-driving car | Fraud detection system | ChatGPT |
| Goal | Simulate human thinking | Learn patterns automatically | Understand and create text |
Benefits and Limitations
Strengths
-
- Saves time and effort.
- Reduces human errors.
- Works 24/7.
- Learns and improves constantly.
-
- Needs lots of data.
- Can be biased or make wrong guesses.
- Works 24/7.Uses heavy computing power.
- Lacks emotional and real understanding.
India’s Growing Role in AI and LLMs
India is becoming a strong player in AI and LLM innovation. From startups to big tech firms, everyone’s building tools in local languages.
Projects like AI4Bharat, Sarvam AI, and Krutrim are developing models that speak Hindi, Tamil, Bengali, and more. These tools help in education, translation, and government communication.
AI is also creating new job roles — in data, automation, and model training — across cities like Bengaluru, Pune, and Hyderabad.
Learning Path — How to Start with AI, ML, and LLMs
Learning Path — How to Start with AI, ML, and LLMs
Want to learn this stuff? Start small.
-
- Learn basic Python.
- Understand data and statistics.
- Take beginner ML courses (NPTEL, Coursera, Kaggle).
- Try small projects — like text or image prediction.
Key Takeaways
-
- AI is the broad concept of smart machines.
- ML helps those machines learn from data.
- LLMs specialize in understanding and generating language.